The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative Is a Model for the Nation
RGGI's functions as a model for other states and regions hoping to reap economic, health, and social benefits in the transition to clean energy we need to combat climate change.
Jessica Russo for NRDC
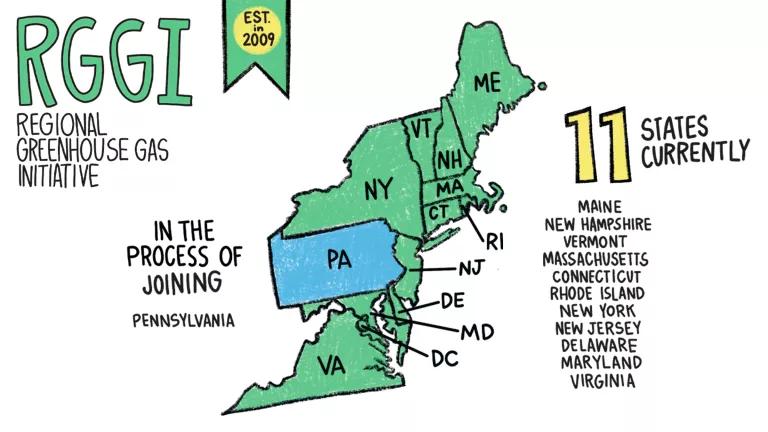
The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (also known as RGGI or “Reggie”) is a pioneering, market-based program to cut climate-altering carbon pollution from power plants in 11 Northeast and Mid-Atlantic states—Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Virginia.
Since its 2009 launch, RGGI has saved consumers hundreds of millions of dollars on energy, with billions more in savings to come; created thousands of new jobs; and improved public health while helping to cut carbon pollution from the region’s power plants in half. RGGI’s well-documented success shows how flexible, market-based approaches to cutting power plant pollution benefit everyone. The program is a model for other states and regions hoping to reap economic, health, and social benefits in the transition to clean energy that we need to solve the climate crisis. Because the RGGI states have agreed to continue cutting carbon pollution through at least 2030, the program’s many benefits will continue for years to come.
Spurred by the program’s success, a growing number of states are participating in RGGI. In recent years, New Jersey and Virginia have joined the RGGI market and Pennsylvania is currently considering joining RGGI as its 12th state. As RGGI expands, its impact on cutting carbon pollution and the benefits it provides across the region will similarly grow.
Through a regular “program review” process that includes technical, economic, policy, and stakeholder review, the RGGI states have also continued to update and improve their programs. Previous program reviews have resulted in more ambitious state commitments to cut carbon pollution and other improvements. In 2021, RGGI states will launch their third program review, giving states and stakeholders a further opportunity to assess the program’s performance and consider improvements.
How RGGI Works

RGGI is a “cap-and-invest” program. Together, the RGGI states set an enforceable regional limit on the amount of carbon pollution that power plants are allowed to emit and sell pollution permits up to this limit through quarterly auctions. RGGI’s design requires large fossil fuel power plants to buy the pollution permits, and the number of permits is lowered each year, so that the region’s power plants contribute progressively fewer emissions to global warming. Auction proceeds are used to generate local and regional economic benefits, including investments in local businesses that provide jobs for residents; weatherization of homes; upgrades of heating and air-conditioning systems; and clean, renewable energy.
How RGGI Pays Off

Cuts Pollution and Improves Health
Just as designed, RGGI has lowered the region’s carbon emissions. In fact, since the program began, RGGI has helped cut carbon pollution from power plants in half. Smart choices by the RGGI states mean that the downward emissions trend will continue, with the pollution cap slated to decline by 3 percent a year through 2030. RGGI has also led to reductions in other dangerous pollutants that pour out of power plant smokestacks alongside carbon pollution. These pollutants—mercury, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter—are linked to human health impacts, including developmental delays, heart attacks, asthma attacks and other respiratory diseases, and even cancer.
A 2017 analysis of RGGI’s first six years found the program created health benefits valued at $5.7 billion. Recent research has shown the program’s health benefits are even larger, including additional health benefits to children—such as reductions in childhood asthma, preterm births, and cases of low birth weight and autism spectrum disorder—as a result of particulate pollution reductions attributable to RGGI.
Creates Jobs and Bolsters the Economy
The cycle of benefits RGGI creates by cutting carbon pollution isn’t just good for our environment and our health. RGGI has also created 45,000 job-years of work across the region since the program’s launch (a job-year equals one year’s worth of full-time employment for one person) and added around $4 billion in economic value to the region. Meanwhile, RGGI state economies have grown 31 percent faster than non-RGGI states, even as the RGGI states have cut power plant carbon pollution nearly twice as fast as the rest of the nation.
Lowers Energy Bills
Thanks to energy efficiency measures and cost-saving renewable energy projects that RGGI helped put in place, consumers in the region have already saved more than $1.2 billion dollars on energy bills so far and will eventually save more than $13 billion on energy over the lifetime of RGGI-funded measures. In RGGI’s first nine years, electricity prices in the region fell by 5.7 percent, even as prices rose by an average of 8.6 percent in other states. Even consumers who don’t participate in energy efficiency programs benefit because participants cut demand overall, which lowers the market price of electricity for everyone.
Virginia, the newest participant in RGGI, has further committed to ensuring equity in its consumer-saving investments by dedicating half of all RGGI proceeds to investments in low-income energy efficiency programs in the state—investments that are expected to total more than $500 million over the next decade and lower energy burdens for struggling families, improving health and lives.
A Model that Works
Modeled on a successful acid rain control program developed under President George H. W. Bush and launched by a bipartisan group of governors, RGGI has enjoyed broad support throughout its history. With its proven track record, RGGI is a powerful example of how states and regions can jumpstart a wide range of economic, social, and health benefits. By moving state and regional economies away from dirty fossil fuels, erratic energy prices, and antiquated power plants and toward clean technologies and innovation, RGGI creates jobs, lowers energy bills, and helps make U.S. businesses more competitive in the global economy.
As other states learn from RGGI’s example, RGGI continues to build on its success. Through a process of regular, public program reviews—one of the hallmarks of the program—the states continue to evaluate and improve the program. In late 2017, the RGGI states successfully completed their second multiyear program review, committing to achieve additional carbon pollution cuts through 2030 and to make other program improvements to capture even more benefits for the region’s consumers, economy, and environment. In 2021, RGGI states will launch their third program review, providing a new opportunity to work with stakeholders to continue enhancing the program.



