India Joins the Paris Agreement on Climate Change
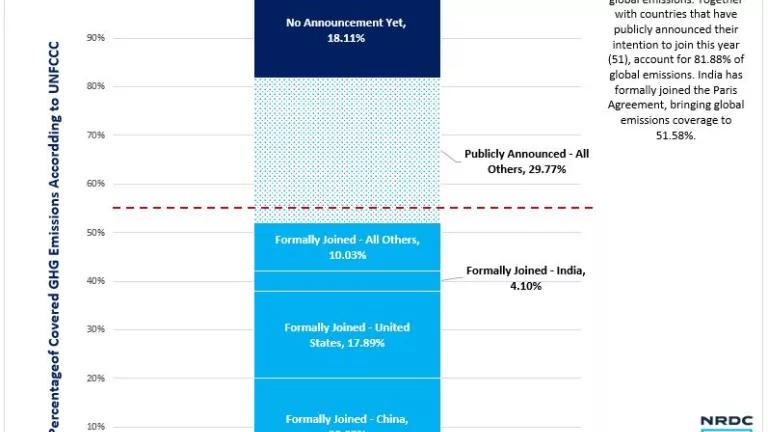
On the birthday of Mahatma Gandhi, India formally joined the Paris Agreement to combat climate change. India’s decision to join signals the commitment to fighting one of the greatest challenges of our time. With India joining, the world is days away from crossing the threshold on ‘Entry Into Force’ for the Paris Agreement. India is the third largest emitter of greenhouse gases in the world. At the same time, India has provided a vision of how low-carbon growth can take place in the future, through ambitious targets for clean energy to meet the needs of its growing economy.
With this step, India signals that it is prepared to continue its efforts to address climate change in the coming years and to strengthen those efforts over time. As a part of the Paris Agreement, India committed to
- Reducing Emissions intensity reduction of 33-35% by 2030 based on 2005 levels
- Target of 40% of electricity from non-fossil fuel based energy sources by 2030 with the support of technology-transfer and climate financing
- Climate adaptation strategy of enhancing investments in development programs in sectors vulnerable to climate change, particularly agriculture, water resources, Himalayan region, coastal regions, health and disaster management.
- To create an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent through increasing forest and tree cover by 2030
India’s ambitious targets are supported by strong government action. In 2015, the Modi government announced 2022 clean energy targets of 175 gigawatts (GW), with 100 GW for solar, 60 GW for wind, and 15 GW for other renewables. The government has also developed energy efficiency programs that will make sure that the majority of India's infrastructure that will exist by 2030 can be built in a more sustainable manner. Recognizing clean energy finance as a major catalyst for achieving its climate targets, India has adopted innovative financial instruments such as green bonds, and is in advanced stages of establishing the nation’s first green bank. Abundant and affordable capital can allow India to rapidly scale up clean energy while enabling continued economic growth.
The Paris Agreement is on the cusp of entering into force. Without the efforts of India, the deal that was reached in Paris would not have been a success, and would not have been able to enter into force faster than anyone anticipated. Now is the time to celebrate this achievement, and to ensure India continues to lead the world in fighting climate change and safeguarding the health and well-being of people in India and all over the world.